Architecture
NoETL uses a server-worker architecture for distributed workflow execution.
Component Overview
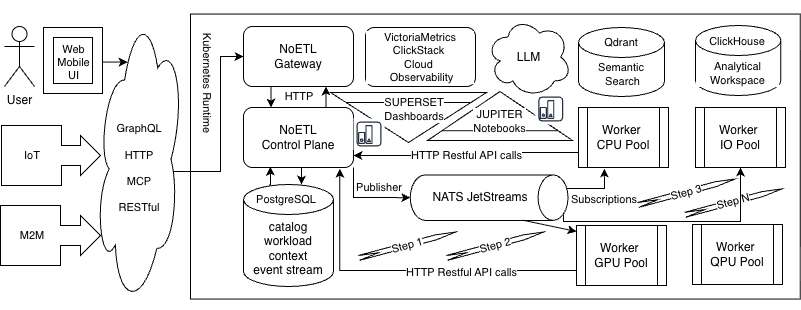
Components
Gateway
Rust-based API gateway for external clients:
- Exposes GraphQL API for playbook execution
- Provides REST API for Auth0 authentication (
/api/auth/*) - Session validation middleware with NATS K/V caching
- Pure gateway design - no direct database connections
- All data access through Control Plane API
- NATS K/V for fast session lookups (sub-millisecond)
- Future: WebSocket subscriptions via NATS for live updates
Session Caching: Gateway checks NATS K/V for cached sessions before calling auth playbooks. On cache miss, playbooks validate from PostgreSQL and refresh the cache.
NoETL Control Plane
Central coordination service:
- Exposes REST APIs for catalog, credentials, executions, and events
- Schedules and supervises workflow executions
- Publishes task notifications to NATS JetStream
- Receives execution events from workers
- Manages retries and backoff policies
- Reconstructs workflow state from event table
- Used by CLIs, UIs, and integrations
Worker Pools
Stateless background executors:
- Subscribe to NATS JetStream for task notifications
- Retrieve task details via Control Plane API
- Run workflow steps and tools (HTTP, SQL, Python, etc.)
- Report events back via Control Plane API
- Scale horizontally based on load
- Isolated execution environments
NATS JetStream
Message broker for task distribution:
- Control Plane publishes task notifications to NATS streams
- Workers subscribe and acknowledge messages
- Messages contain pointers to Control Plane API for task details
- Durable subscriptions ensure no task loss
- Supports multiple worker pools and load balancing
Catalog & Credentials
Storage for workflow definitions:
- Catalog: Playbooks, versions, schemas, tool definitions
- Credentials: Connection configs and tokens with scoped access
Event Bus and Telemetry
Observability infrastructure:
- Every step emits structured events (start/finish/errors, durations)
- Events exported to analytics backends (ClickHouse, VictoriaMetrics)
- Vector stores (Qdrant) for AI-assisted optimization and semantic search
Storage/Compute Integrations
Connectors for external systems:
- Warehouses: DuckDB, PostgreSQL, ClickHouse, Snowflake
- Files/Lakes: GCS, S3, local filesystem
- Vector DBs: Qdrant
- External services: HTTP APIs
Data Flow
┌─────────────┐ ┌─────────────┐ ┌───────────────┐ ┌─────────────┐
│ Web UI │────▶│ Gateway │────▶│ Control Plane │────▶│ NATS │
│ (GraphQL) │ │ (Rust) │ │ (FastAPI) │ │ JetStream │
└─────────────┘ └─────────────┘ └───────┬───────┘ └──────┬──────┘
│ │
┌─────────────┐ │ ┌─────▼─────┐
│ CLI/API │─────────────────────────────────┘ │ Workers │
│ (Direct) │ │◀─────────────│ (Execute) │
└─────────────┘ │ (events) └───────────┘
▼
┌─────────────┐
│ PostgreSQL │
│ (Events) │
└─────────────┘
- Web UI sends GraphQL requests to Gateway
- Gateway authenticates and forwards to Control Plane API
- CLI/API can also call Control Plane directly
- Control Plane validates, creates execution, publishes task to NATS
- Workers receive NATS message with task pointer
- Workers fetch task details from Control Plane API
- Workers execute steps and report events to Control Plane API
- Control Plane stores events in PostgreSQL
noetl.eventtable - Control Plane monitors events to determine next steps in workflow
Database Schema
The NoETL PostgreSQL schema is intentionally simple - no queue tables:
| Table | Purpose |
|---|---|
catalog | Playbook definitions (path, version, content) |
event | Execution events (status, results, errors) |
credential | Encrypted credentials |
keychain | Runtime token cache with TTL |
transient | Execution-scoped variables |
runtime | Worker pool and server registration |
schedule | Cron/interval scheduled playbooks |
Control loop: Control Plane analyzes event table to reconstruct execution state and determine next steps, then publishes tasks to NATS.
Communication Patterns
Control Plane → NATS → Worker
Task distribution via NATS JetStream:
- Control Plane publishes task notification to NATS stream
- Message contains execution_id and task pointer (not full payload)
- Worker subscribes, receives message, acknowledges
- Worker calls Control Plane API to get full task context
- Worker executes and reports events to Control Plane API
Event-Driven State
All execution state is persisted as events in PostgreSQL:
- Server reconstructs workflow state from
noetl.eventtable - Determines which steps completed, which are pending
- Publishes next tasks to NATS based on workflow graph
- Enables replay, debugging, and distributed execution
Scaling
Horizontal Scaling
- Workers: Add more worker replicas for throughput
- Server: Single server coordinates all executions
- Database: PostgreSQL handles concurrent access
Resource Pools
Configure worker pools for different resource types:
- CPU-intensive workloads
- GPU workloads (future)
- I/O-bound operations
See Also
- Design Philosophy - Architectural principles
- Observability Services - Monitoring stack
- Multiple Workers - Worker configuration